Digestive System
Be able to name the major organs of the digestive system, the major types of tissues found in each, the membranes associated with each, and give the functions of each. 
The view below illustrates the relative length of each portion and the tube-within-a -tube configuration. 
At the junction of the stomach, the epithelium abruptly changes to simple columnar. Within the deeper layers of the mucosa, are many glandular cells. The outer membrane is the serosa, which is composed of simple squamous epithelium and connective tissue. 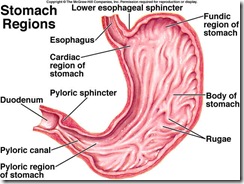
What are the digestive contributions of the pancreas? What are the endocrine functions, and how are they related to digestive processes? 
Be able to identify the four lobes of the liver, and give the functions of the liver and gall bladder. 
Explain the functions of each cell type within the lobules. Lining the sinusoids are monocytes, which are called Kupffer cells or stellate reticuloendothelial cells (stellate = star shaped; reticulo = framework; endothelial = line the inner cavity). 
From looking at these drawings, what would you guess constitutes a hepatic triad? 
Note that the covering of the abdominal viscera (visceral peritoneum) is continuous with the lining of the abdominal wall (parietal peritoneum). However, each region has a different name. The portion of the mesentery between the liver and stomach is the Lesser omentum, and the portion supporting the colon is the mesocolon. Midsagittal view. 
Frontal view of greater omentum. 
Note modification of internal surface area of intestines by folds, villi, and microvilli. Each modification of the internal surface of stomach and intestines increases surface area for both secretion of enzymes, water, mucus, etc., and for absorption of nutrients, which must be broken down into their molecular building blocks. 
Micrograph of intestinal villi. 
Drawing of microvilli. 
Electron micrograph of microvilli. 
The plicae are found within the walls of the jejunum, the middle portion of the small intestine. These folds subdivide the intestine into segments. Segmental digestive movements of chyme occur when the remnants of food and digestive juices are mixed back and forth within these intestinal "segments." 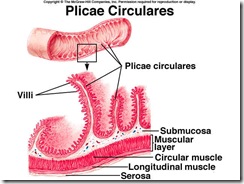
The lining of the ileum (not shown) lacks plicae and villi. An ileocecal valve controls entry into the colon. The vermiform appendix is a vestigial portion of the cecum, found in humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans. 
The tenia coli are three remnants of longitudinal muscles. 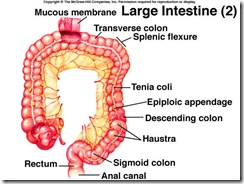
The muscular layer below is made up of a circular layer only. 
Goblet cells secrete mucus.
Connect With Medical Show
Medical show Youtube
Popular post
-
ا لحمد لله رب العالمين بفضل الله اجتزت اليوم امتحان الايلتس وحصلت علي سكور 8 أود أن اشارككم تجربتي لعلها تفيد احد الزملاء أول...
-
Pyramidal Pathway I) Cortico spinal tract: It arises from Betz cells in area 4, and then descends: 1- In the corona radiata . 2- ...
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common silent and invisible sexually transmitted disease, that lead to genital warts and...
-
Pitutary dwarfism Made easy, Simple , simplified . Etiology : Congenital: agenesis, aplasia, dysplasia. Traumatic. Infection:...
-
1. Good personal hygiene 2.Avoid sun exposure as sun exposure makes the fungal infection more apparent. 3.Wear cotton clothing a...
-
Can your eyes make you sick?: Investigating the Relationship between the Vestibulo-ocular Reflex and Virtual Reality Mark H. Draper 29 A...
-
a colonoscopy - 3D Medical Show A colonoscopy is a test where an operator (a doctor or nurse) looks into your colon. The colon is some...
-
Simple Mnemonics for Clinical picture of cretinism hypothyroid face with protruded tongue at birth & early neonatal : 1- F...
-
This is illustrated atlas for pediatrics in neonatology click on picture for zoom+
Support :
Creating Website | Johny Template | Mas Template
Copyright © 2011. Medical Show - All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2011. Medical Show - All Rights Reserved
Template Created by Creating Website Published by Mas Template
Proudly powered by Premium Blogger Template
Proudly powered by Premium Blogger Template











Post a Comment