Def.: Hydrodynamic disturbance of CSF vol. Of CSF within ventricular System
Types:
with or without concomitant in its tension.
1- Normal pressure hydrocephalus only male.
2- Communicating hydrocephalus
3- Non-communicating hydrocephalus ( obstructive ) : i most common
4- Arrested hydrocephalus
Causes (pathogenesis) :
(A) Hydrocephalus e` CSF pressure:
1- secretion: - choriod plexus ( congestion – tumor )
- vit. A ( hyper – hypo )
- Idiopathic
2- Obstructive : (i commonest)
| Congenital | Acquired |
| A Agenesis of foramen of monro - Arnold chiari type II syndrome | * Post – inflammatory: meningitis. * Post-traumatic * Neoplastic : i commonest post. Fossa tumors |
| B Bicker Adam's syndrome | |
| C Congenital toxoplasmosis | |
| D Dandy walker malformation |
+ Most common : X-linked hydrocephalous ( aqueductal stenosis )
Malformation of vein of gallen ( A.V. fistula – High COP failure – arterial bruit on frontal
& parietal bone auscultation ).
3- Impaired absorption:
* Subarachnold space: ( adhesions – leukemia infiltration ).
* Dural sinus thrombosis.
B- Normal pressure hydrocephalus:
* Congenital cerebral agenesis.
* Diffuse cerebral Atherosclerosis.
* Dementia as Alzheimer.
C/P
(A) Before closure of ant. Fontanel:
Head
- - head circumference
- - Delayed closure of a. Font.
- - Wide separation ( ) sutures
- - Craniotabes
- - Mc Ewen sign :i cracked pot sound on percussion.
- - Arterial bruit:
- Malf. of vein of gallen.
- - Fore shortened occiput: Arnold chairi syndrome
- - Prominent occiput: dandy walker syndrome
+ Over stretched & glistening scalp.
Eye:
- * Sun set appearance.
- * Medial squint.
- * Visual disturbance & optic atrophy & papilledema.
Back:
- * Spina bifida.
- * Meningocele
Neurological manifestations :
- * No of ICT
- * Late cases:
- - Mental retardation.
- - Motor retardation ( spastic paraplegia ).
- - + ve babinski.
- - Convulsions.
b) After closure of A.F.
- * Head enlargement less significant
- * Manifest of ICT . . . .
- * Abducent ( 6th ) nerve palsy ( medial squint )
- * Personality change
Investigation :
1- X-ray (plain):
| Bfore closure | After closure of A.F. |
| Cranio-facial disproportion | Signs of ↑ ICT |
| Wide speta ( ) sutures | Finger print appearance |
| Thinning of skull bone | Beaten silver appearance |
2- CT & MRI: brain ( i best )
3- CSF study : ( cytoalbminous Dissociation )
4- Blood examination.
5- Arteriography
6- U/S : through ant. Fontanel
7- ECG : for convulsions.
D.D.: Other causes of macrocephaly:
* Skull causes: rickets – osteogenesis imperfecta Ch. Hemolytic anemia .
* Meningeal causes: subdural hematome – effusion.
* Brain causes : Hydranencephaly , megalocephaly ( neurofibromatosis ).
* Familial.
Treatment:
A- Medical:
* Indication: in cases of CSF production.
* Mech: - Salt & H2O restriction.
- Diamox.
- Isosorbide CSF absorption.
B- Surgical:
1- Choroid plexectomy: in papilloma.
2- Diathermy coagulation: of choroid Plexus.
3- Opening of stenosed aqueduct: high morbidity.
4- Endoscopic fenestration of 3rd ventricular Floor.
5- Excision of brain tumor.
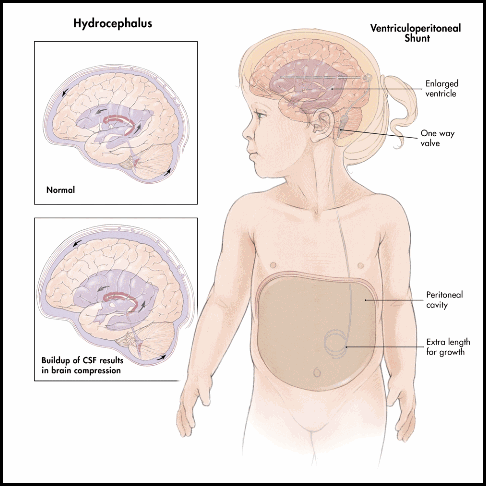
6- Shunt operation:
* I commonest operation.
* Using one way valve ( spitz – halter valve ).
| Types | Indications |
| 1- Ventriculo-ureteral 2- Ventriculo-atrial 3- Ventriculo-pleural 4- Ventriculo-peritoneal (most common) 5- Lumbo-peritoneal. 6- Torkilidsen shunt. Complications: Obstruction of tube. Infection . Rejection. Shortening of i tube e` age. | 1- Progressive head enlargement. 2- Obstructive hydrocephalus. 3- No: - Eye complication - neurological Manifestation - mental affection - ass e` cong. Malformation |
Complications:
| Due to hydroceph. Progression | Medical ttt | Surgical ttt |
| Eye: (Visual dist. – medial squint – papilloedema, optic atrophy – compress on optic chiasma. | - Electrolyte dist. - Metabolic acidosis | 1- shunt.... 2- V-P: peritonitis. 3- V-A: endocarditis. 4- L-P: radioculopathy |
| Neuro: ( MR.- UMNL, gait disturb- convulsions – post. Cerebr. art occlusion |
N.B.: CSF.:
* Volume: (adult 120 ml – infant 50 ml ).
* Pressure (180-200 mm H2O = 18 – 20 mm/Hg)
This is visual diagnosis case about hydrocephalus














Post a Comment